Tetra-PEG gel
Hydrogels are 3D polymer network swollen in water. Thus, the composition of hydrogels is similar to that of soft tissue.
This similarity supports the use of hydrogels as biomaterials.

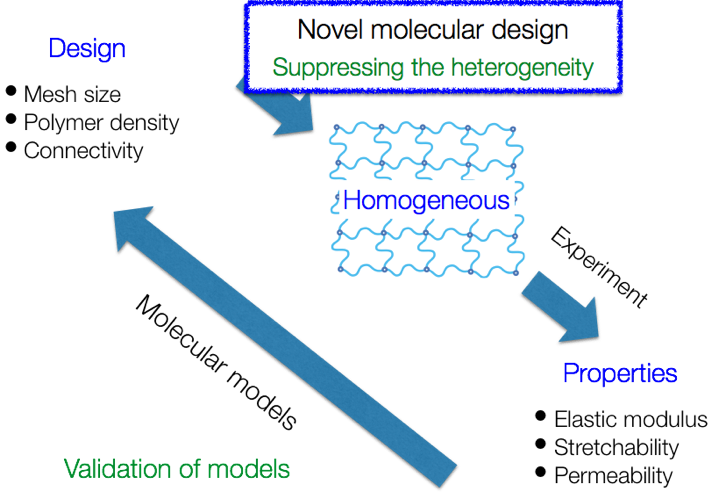
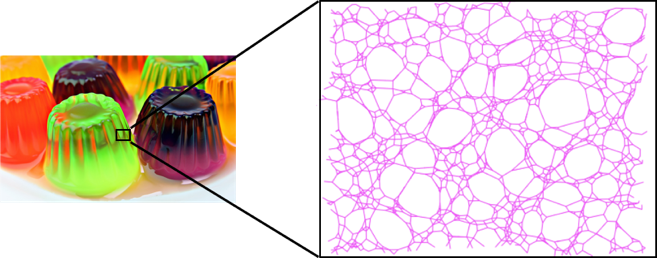
Biomaterials must achieve multiple properties at once for the application as in-vivo-used biomaterials. Thus, it is important to precisely control over physical properties of hydrogels. Of course, we can control these properties by controlling over polymer network structure of hydrogels. However, in general, polymer networks have heterogeneous network structures, and are hardly controlled. Therefore, it has been difficult to precise control of physical properties of hydrogels.
Hydrogel, made by Toyoichi Tanaka
Ronnie Coleman, from his instagram
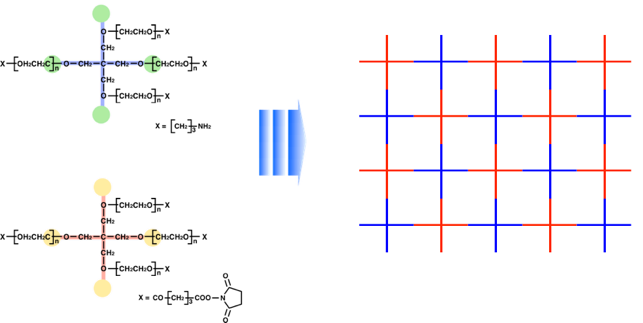
Recently, we have, for the first time, developed a novel hydrogel with extremely homogeneous polymer network. The hydrogel is formed from two mutually reactive four-armed prepolymers. We named the hydrogel Tetra-PEG gel, which has backbone of polyethyleneglycol (PEG). Because Tetra-PEG gels have defined network structure, they are promising system for understanding the structure-properties relationship of polymer gels. One of our final goals is to understand the fundamentals of polymer gels.
Heterogeneous network structure
Tetra-PEG gel